By Katherine Kozlowski, Medical Author and Contributor to Vein News and www.VeinsVeinsVeins.com
What is the Klippel Trenaunay Syndrome ?
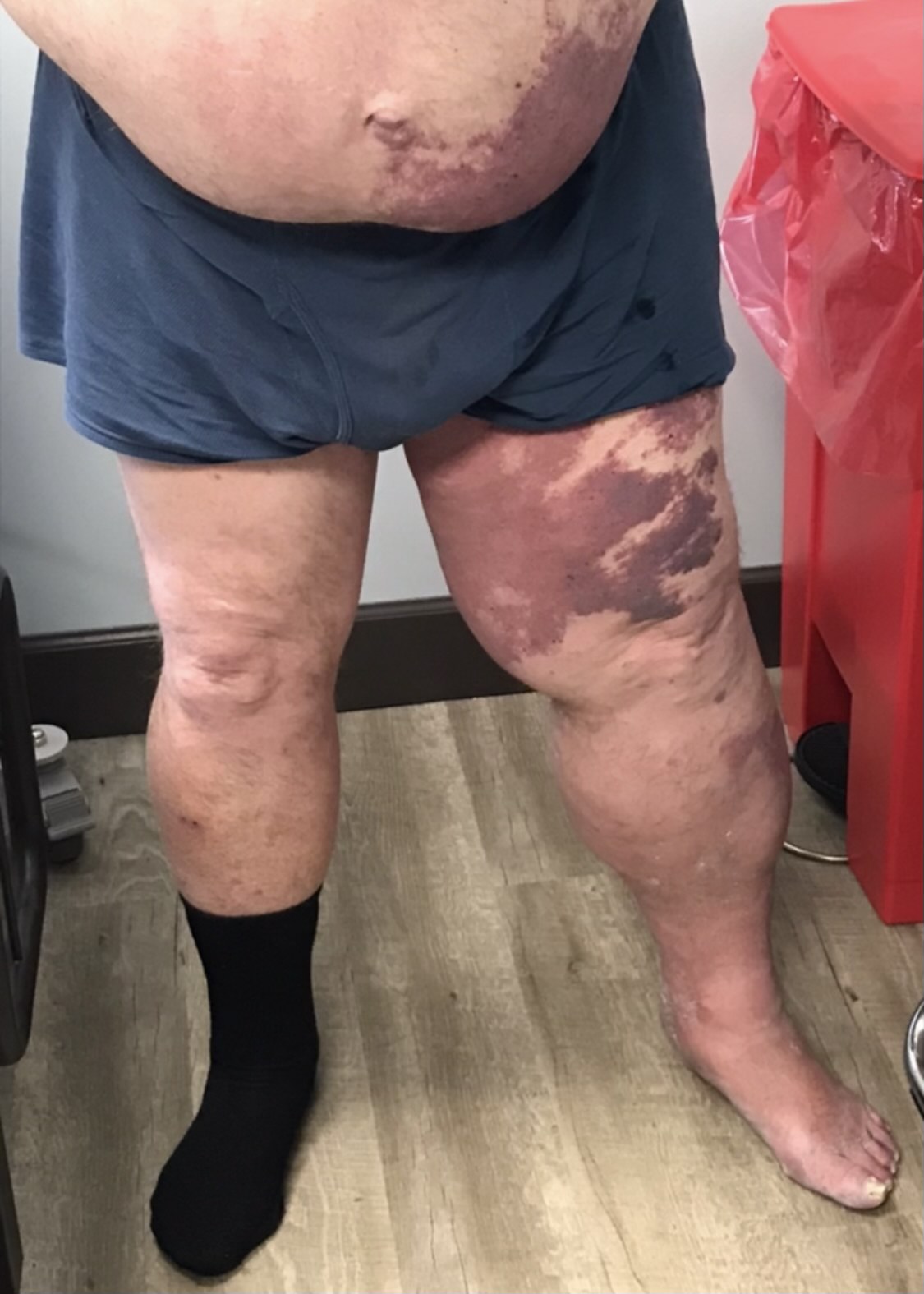
The Klippel Trenaunay syndrome (KTS) is a rare and sporadic congenital disorder, characterized by the classical triad of port-wine stains, varicosities along with bone and soft tissue hypertrophy.
How common is the Klippel Trenaunay syndrome?
Klippel Trenaunay syndrome (KTS) is a very rare congenital vascular anomaly and is estimated to occur in 1 in 320,000 live births.
What is the genetics of the Klippel Trenaunay syndrome?
According to John B Mulliken MD, Boston Children's Hospital, KTS occurs from "a mutation in primitive cells that form a limb that are destined to become blood and lymphatic vessels, fat, and bone. This is a somatic mutation in the PIK3CA [gene]. This genetic alteration does not occur in germ cells and therefore, it cannot be passed on to the next generation or subsequent generations.
What is a somatic mutation?
A somatic mutation occurs in a single cell in developing somatic tissue. That mutated cell is the progenitor of subsequent cells of identical mutations, all of which have descended from the originally mutated cell.
Are somatic mutations ever passed on to progeny?
No. It is impossible because somatic cells by definition are those that are never transmitted to progeny.
What types of symptoms do patients get with the Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome?
Leg pain, swelling, lymphedema, bleeding, superficial thrombophlebitis, and deep vein thrombosis.
What are the diagnostic tests that are used to diagnose the vascular abnormalities/anomalies in the Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome?
Noninvasive imaging techniques and sometimes, invasive venography are used for the diagnosis and evaluation of the disease in patients.
In patients who need venous interventions, Doppler ultrasound (US), contrast-enhanced MR imaging, and venography are used to assess the anatomy of the target vessels and the patency of the deep venous system.
https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/klippel-trenaunay-syndrome/